
Is oatmeal good for irritable bowel syndrome? This question gains relevance as more people struggle with the complications of IBS and the dietary challenges it brings. Given the varied symptoms of IBS, finding foods that do not exacerbate the condition is crucial. Oatmeal, known for its soluble fiber and gut health benefits, emerges as a potential ally in managing IBS symptoms effectively.
At Nudge, a digestive health supplement company, we understand the complexities of digestive disorders like SIBO, a common form of IBS. Our all-in-one supplement addresses the three root causes of SIBO, including gut motility, core nutrition, and stress, without needing a prescription. Combining dietary management with effective supplementation can significantly enhance digestive health.
Rooted in our comprehensive scientific analysis, we've put together this guide that explores the impact of oatmeal on IBS. We will compare the effects of different types of oats, look into alternatives, and provide practical tips for safely incorporating oatmeal into your diet. By the end, you'll clearly understand the question, "Is oatmeal good for irritable bowel syndrome?" to mitigate IBS symptoms, improve bowel movements, and enhance overall digestive health.
Let's jump in!
Is Oatmeal Good for Irritable Bowel Syndrome?
Is oatmeal good for irritable bowel syndrome? This question often surfaces when discussing the dietary management of IBS. Understanding the impact of oatmeal on your digestive system is crucial. Experts say oatmeal, rich in soluble fiber, can soothe the gut and alleviate symptoms of IBS.
Incorporating oatmeal into a low FODMAP diet can benefit individuals with IBS. Soaking oats overnight with almond milk makes them easier to digest, which can reduce digestive issues. Adding oat bran further increases the fiber content, which is suitable for managing bowel disease and keeping a healthy gut. While oatmeal is generally safe for people with IBS, overeating can cause stomach pain and other symptoms.
For individuals with gluten sensitivity or celiac disease, it's essential to choose oat products labeled as gluten-free to avoid contamination. Pairing oatmeal with maple syrup, peanut butter, or a splash of lactose-free milk can make it a nutritious and tasty part of your IBS diet.
Nutritional Profile of Oatmeal
Oats, widely recognized for their health benefits, are a nutritious staple in many diets. This whole grain is a traditional breakfast choice and a smart addition to any diet, especially for those managing irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).

Nutritional Content of Oats:
- Manganese: Provides 63.9% of the daily value (DV).
- Phosphorus and Magnesium: Each offers 13.3% of the DV.
- Copper: Accounts for 17.6% of the DV.
- Iron: Offers 9.4% of the DV.
- Zinc: Delivers 13.4% of the DV.
- Folate: Supplies 3.2% of the DV.
- Vitamin B1 (Thiamin): Offers 15.5% of the DV.
- Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid): Provides 9.1% of the DV.
- Additional Nutrients: Include small amounts of calcium, potassium, vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), and vitamin B3 (niacin).
When prepared, one cup of oatmeal (from half a cup of dry oats) typically contains:
- Carbs: 27.4 grams
- Protein: 5.3 grams
- Fat: 2.6 grams
- Fiber: 4 grams
- Calories: 153.5
Oats are beneficial for the gut, particularly for individuals with IBS. The soluble fiber in oats, particularly beta-glucan, helps regulate bowel movements and ease symptoms of IBS. This type of fiber aids in softening stool, making it easier to pass and reducing discomfort in the small intestine. Moreover, resistant starch in oats supports the growth of beneficial gut microbes, further contributing to gut health.
How Do Oats Affect IBS Symptoms
Oats offer various benefits for managing irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), but understanding their impact requires knowing the type and amount of oats ingested. Here's how different forms of oats influence IBS symptoms:
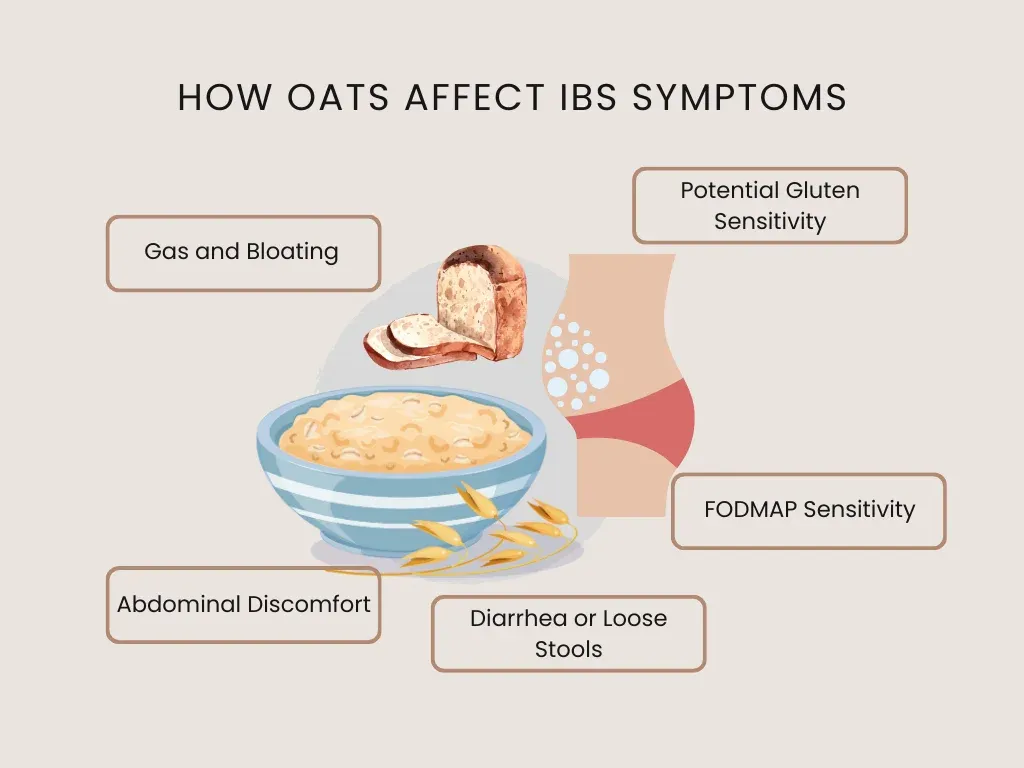
Gas and Bloating
Gas and bloating are common symptoms for many people suffering from IBS. The soluble fiber in oats may help by absorbing water to regulate bowel movements. However, fiber from raw oats or oat flour can ferment in the large intestine, which might lead to more gas and bloating. Dietitians recommend that individuals should start small in serving size for oat products while gradually increasing them over time so as not to overwhelm their gut bacteria.
Abdominal Discomfort
People with IBS find belly pain extremely difficult. Oats are generally recommended for their stomach-calming properties, but the type of fiber matters. When mixed with liquid, the soluble fiber in oatmeal becomes a thick gel in the bowel, relieving discomfort and soreness. Nevertheless, you must observe how their bodies react to this food and alter the amount accordingly.
Diarrhea or Loose Stools
Oats can help solidify loose stools or, in some cases, lead to diarrhea. The effect depends on the individual's specific IBS type and how their body processes the fiber in oats. Oatmeal's ability to absorb excess liquid in the gut can aid those with diarrhea-predominant IBS, but starting with small amounts is key to understanding its impact.
Potential Gluten Sensitivity
While oats are naturally gluten-free, cross-contamination with gluten-containing grains can occur during processing. For IBS sufferers with coeliac disease or gluten sensitivity, consuming oat products labeled as gluten-free, like gluten-free oat flour or instant oats, is crucial to avoid triggering symptoms.
FODMAP Sensitivity
FODMAPs are a group of carbohydrates that can ferment in the gut and cause symptoms in IBS patients. Although oats have a low FODMAP content, portion sizes must be strictly adhered to. Overeating oatmeal can increase the load of FODMAPs and symptoms. Before establishing which variety and amount of oats are suitable for an IBS-friendly diet, it is important to consult a healthcare provider or a dietitian.
Different Types of Oats and Their Suitability for IBS

When exploring whether oatmeal is good for IBS, it's crucial to consider the various types of oats and how they might affect those with IBS. Oats, in general, are a staple recommendation for their high fiber content, which can aid digestion. However, the specific type of oats may significantly affect how well individuals manage their IBS symptoms.
Steel Cut Oats
Steel-cut oats retain more natural texture and nutrients because they are minimally processed. They offer a robust option for those managing IBS, as they slowly digest and are less likely to trigger symptoms. The benefits of oatmeal for IBS include the gradual absorption of fiber, which can regulate digestion without overwhelming the gut.
Rolled Oats
Rolled oats are slightly more processed than steel cut but still retain much of their fiber. They are pre-steamed and then rolled, which helps in quicker cooking. For individuals considering oatmeal for managing irritable bowel syndrome, rolled oats offer a balance between ease of preparation and maintaining enough fiber to aid digestion without causing significant discomfort.
Instant Oats
Instant oats undergo more processing, which significantly reduces their fiber content. While they are the quickest to prepare, the impact of oatmeal on IBS can vary when consuming instant types. They might digest too quickly, potentially leading to a spike in symptoms for some IBS sufferers. Those wondering if oatmeal suits IBS sufferers might find instant oats less beneficial than their less-processed counterparts.
Oat Bran
Oat bran, though not a type of oatmeal, is derived from the outer layer of the oat grain. It is rich in soluble fiber, which can be particularly helpful in managing IBS symptoms. Oat bran might be an alternative for those who find regular oatmeal too coarse or irritating. The role of oatmeal in IBS diet plans often incorporates oat bran for its gentler effect on the gut.
5 Oat Alternatives to Manage IBS Symptoms
IBS affects many people, leading them to seek diet adjustments to manage symptoms. While oatmeal is often recommended due to its high fiber content, it might only suit some with IBS. This section explores five alternatives to oatmeal that can help manage IBS symptoms effectively.
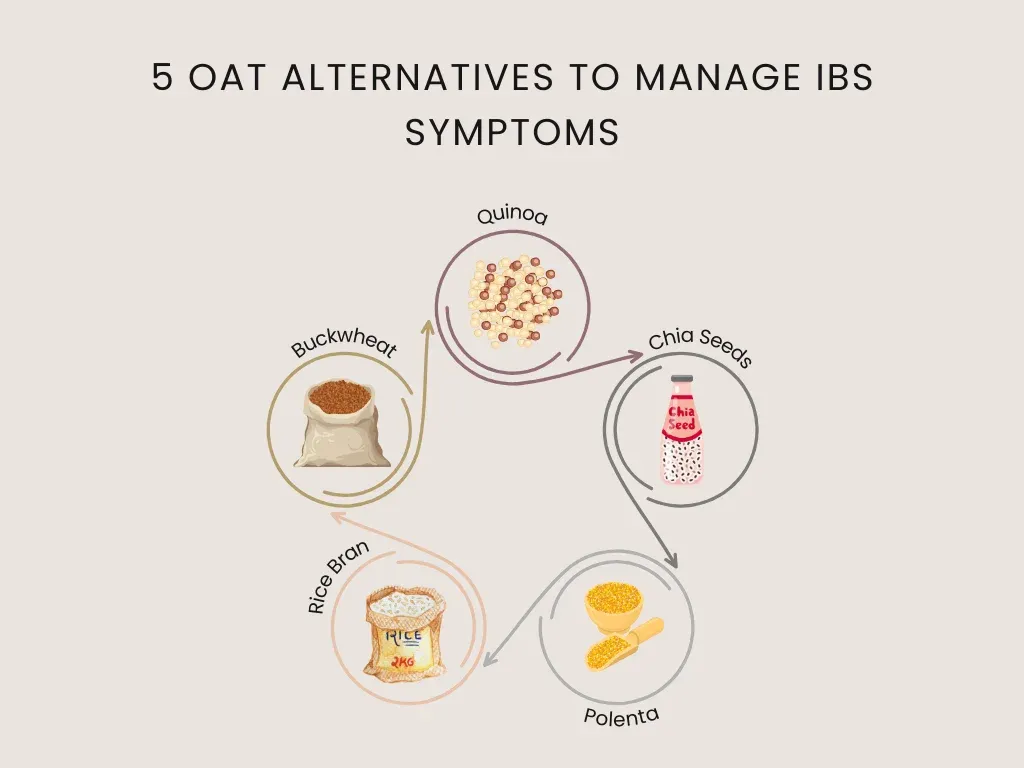
1. Quinoa
Quinoa is a superb substitute for oatmeal if you have IBS. It is a gluten-free seed with all nine essential amino acids for complete protein. The rich dietary fiber in quinoa can be used by persons allergic to IBS and may also control bowel movements. Moreover, quinoa contains both insoluble and soluble fibers. Hence, it is more easily digested than oatmeal, so it’s less likely to cause any symptoms because it only contains insoluble fiber.
2. Buckwheat
Unlike wheat, buckwheat is gluten-free and can be consumed by people with IBS who are sensitive to gluten. It is an effective alternative to porridge because it contains both types of fiber that improve digestion without irritating the intestines. Besides, buckwheat has a strong taste and provides a sense of satisfaction when taken for breakfast.
3. Rice Bran
To those with IBS, rice bran is a non-abrasive oatmeal alternative due to its high dietary fiber content. It promotes easier digestion and helps reduce the two frequent symptoms of IBS like constipation and diarrhea. Mixing it up with low-FODMAP fruits or a little yogurt will make it more nutritious and gut-friendly in the morning.
4. Polenta (Corn Grits)
Polenta, or corn grits, is another suitable oatmeal substitute for those managing IBS. It is naturally gluten-free and offers a source of antioxidants and essential minerals. Polenta is good on the stomach, and its creamy texture can be a comforting start to the day. It’s essential to ensure it's cooked softly and seasoned minimally to avoid potential IBS triggers.
5. Chia Seeds
Chia seeds are small but mighty in terms of nutritional benefits, particularly for IBS management. These seeds contain high levels of omega-3 fatty acids and swell up in the stomach, creating a gel-like material that helps with the passage of stool. For this reason, they are also a suitable replacement for oatmeal, particularly for those with IBS who suffer from constipation.
5 Tips When Incorporating Oatmeal into Your IBS Diet Plan
When it comes to managing IBS, diet plays a pivotal role. It helps harness the benefits of oatmeal for IBS without undue discomfort. Here are five practical tips for integrating oatmeal into your IBS management plan:

Tip 1: Start with Small Servings
When trying oatmeal for irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), start with a small amount to see how your digestive system reacts. It may take time for your digestive system to get used to it. Eating only a little oatmeal at first can help you see if it affects your IBS in any way. If your symptoms improve, try a larger portion next time. Making gradual changes will stop any sudden shifts from causing discomfort.
Tip 2: Choose the Right Type of Oats
Not all oats are created equal, especially when considering oatmeal's effects on irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Rolled and steel-cut oats generally benefit IBS sufferers more than instant varieties. The less processed the oats, the higher their fiber content, aiding digestion and reducing IBS symptoms. Selecting the correct type of oats can significantly affect how oatmeal impacts IBS.
Tip 3: Monitor Your Fiber Intake
While having enough fiber for good digestion is important, having too much can worsen your IBS symptoms. When incorporating oatmeal into your diet, be mindful of your overall fiber intake. This means if you eat oatmeal, which is very high in fiber, try having less-fibrous foods during the day so that your total daily intake remains within levels. You must understand what adjustments are made to an IBS diet that includes oatmeal to keep everything under control.
Tip 4: Customize Your Oatmeal
Adjusting your oatmeal can be more helpful for an IBS diet. Do not include high-FODMAP fruits or fake sugars since they may lead to symptoms. Instead, put some slices of banana or a little cinnamon, which are safe for flavor intensification without worsening IBS signs. The advantages and risks of oats for IBS can be influenced by the method used in preparing them and the extent to which they are customized.
Tip 5: Listen to Your Body
Everyone with IBS reacts to foods in their own way, including oatmeal. After eating oatmeal, take note of how your body reacts to it. If the symptoms worsen, you may need to change the quantity taken or try another kind of oats. Oatmeal affects people with IBS differently, and thus, you must pay attention to what your body tells you to manage the condition well.
Frequently Asked Questions
These questions often arise among those managing this condition. Let's address some common inquiries:
Can oatmeal help with IBS symptoms?
Yes, oatmeal contains a lot of soluble fiber that provides benefits to people with IBS. This fiber can slow digestion, which might control diarrhea and make bowel movements more regular. Both are common problems among those who suffer from this condition.
How does oatmeal affect IBS?
Oatmeal can positively impact IBS by stabilizing bowel movements and reducing symptoms like abdominal pain and bloating. Adding oatmeal to your diet is crucial to ensure it does not exacerbate symptoms. This helps your body adjust without overwhelming the digestive system.
Is oatmeal suitable for IBS sufferers?
For most individuals, managing their IBS with oatmeal should be fine. Due to its high solubility and low gluten, oats are considered one of the safest grains for these patients. However, individuals must monitor their reactions to oatmeal, as tolerance can vary widely. Starting with plain oatmeal and avoiding high FODMAP toppings like honey or certain fruits can also be crucial in maintaining symptom control.
Key Takeaway
Is oatmeal good for irritable bowel syndrome? Oats may help some with IBS. The fiber in oats could help make digestion better. But not all people with IBS react the same way to oats. Slowly add oats to your diet and see how your body responds. How you make oatmeal can also affect whether it helps with IBS symptoms or not.
Personalized dietary adjustments are crucial to managing IBS effectively. Oatmeal can be part of an IBS-friendly diet, but its suitability depends on your condition and tolerance. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help tailor your diet to your needs, ensuring you include the right balance of IBS-friendly foods like oatmeal.
Many people wonder, "Is oatmeal good for irritable bowel syndrome?" While oatmeal can aid in symptom management for some, it might aggravate digestive symptoms in others. If you’re considering oatmeal for bowel disease relief, try exploring probiotic vitamins and SIBO supplements, like Nudge, which complement dietary approaches to alleviate IBS symptoms.